Coaxial Cables
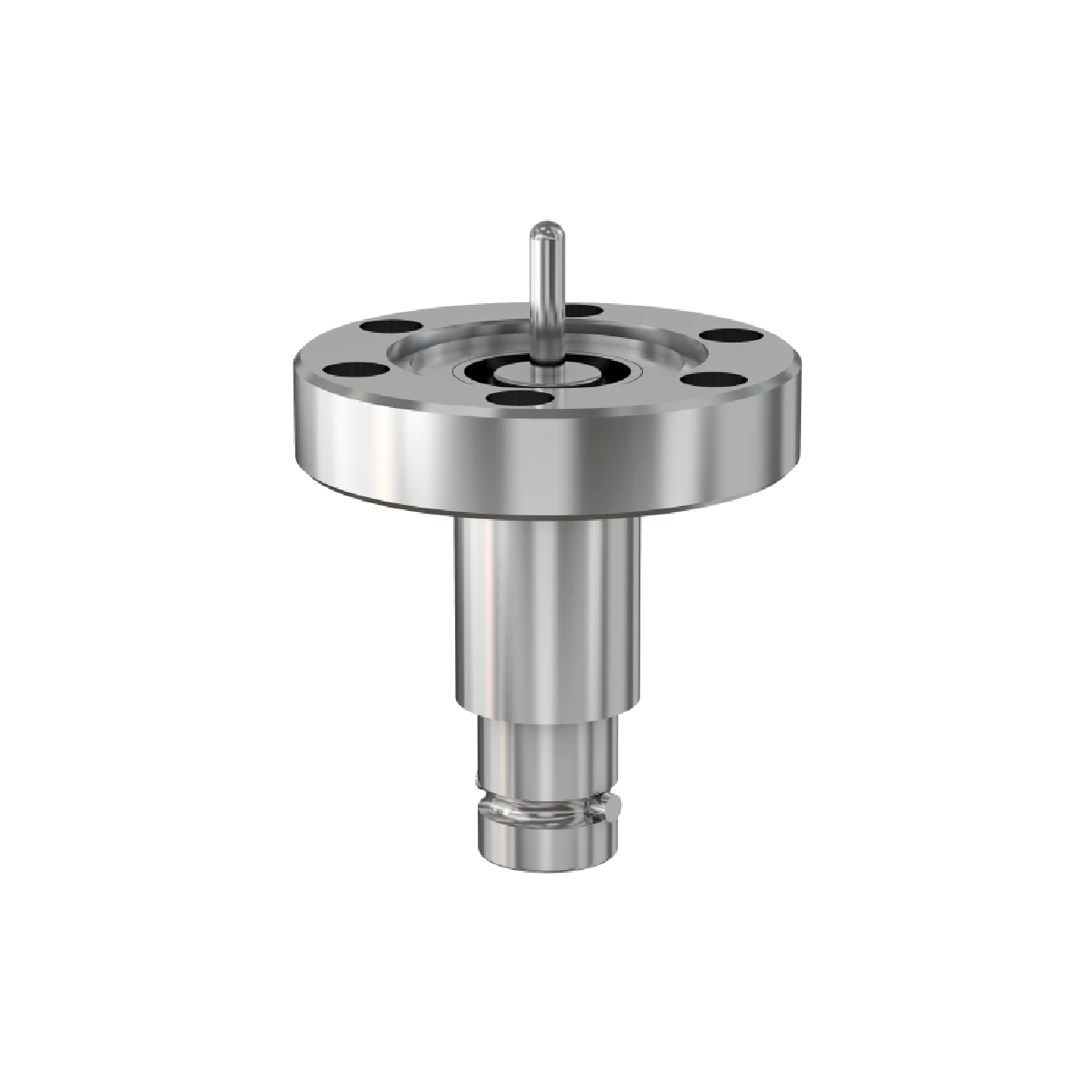
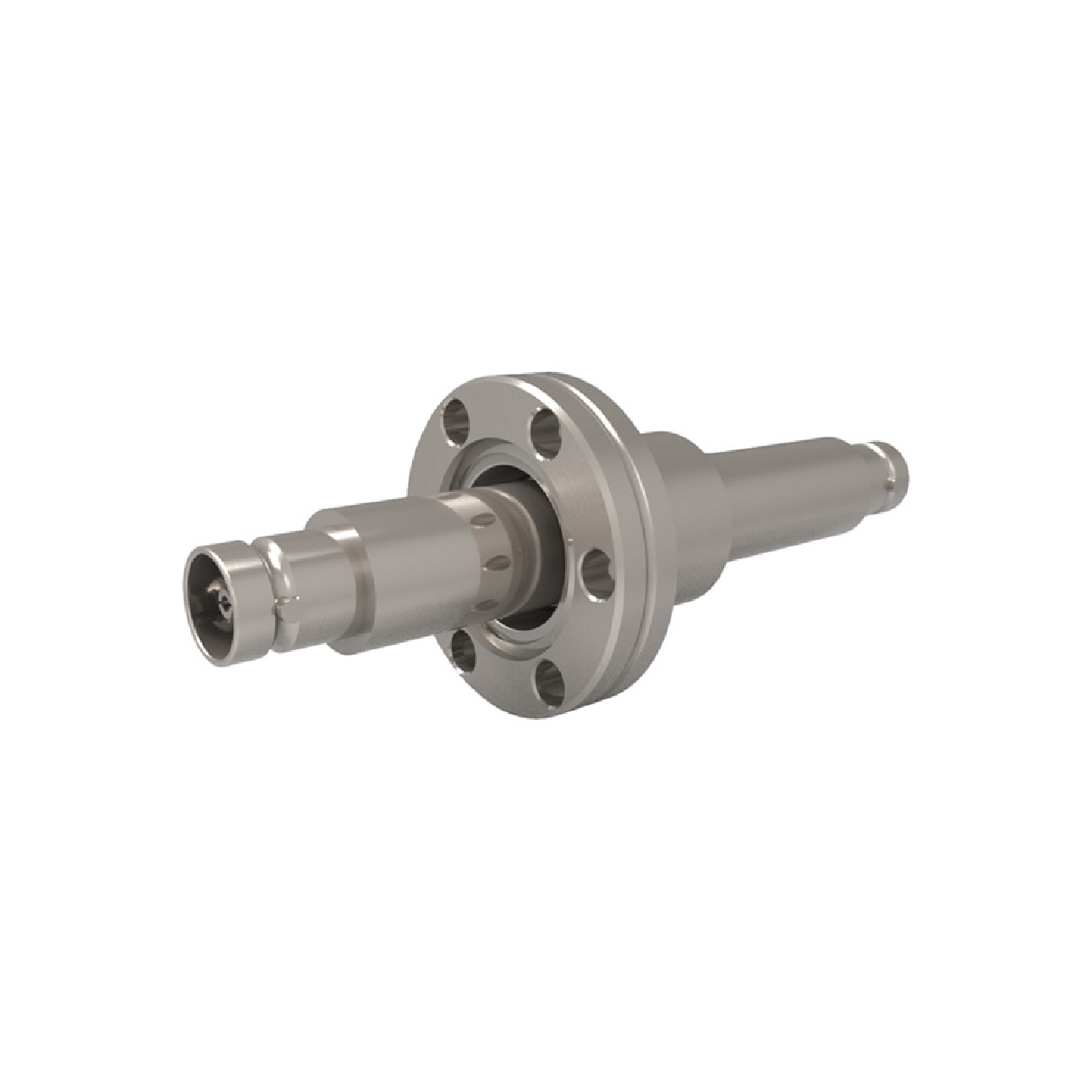
Coaxial Feedthroughs
A coaxial cable has a center conductor insulated from a conducting outer shield which blocks electrical noise, providing stable and repeatable signals.
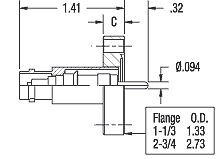
Designed to transfer low-current, low or high-voltage signals from low or high-impedance sources across the vacuum wall. The main characteristic is impedance (set by conductor diameters, spacing, and dielectric constant) and is not a function of length.
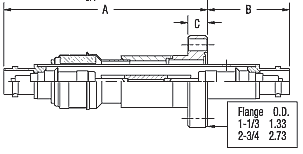
- Double-ended: Use when continuous RF shielding through air ↔ vacuum is required.
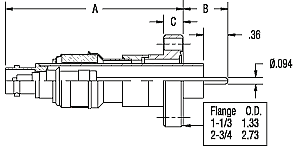
- Single-ended: Use when continuous shielding is less critical.
- BNC: 50 Ω / 75 Ω, low-power transmission lines.
- MHV: Medium power with high-voltage requirement; pins are exposed.
- SHV: High-voltage; male/female contacts are recessed for safety when disconnected.
Multiple conductors are available depending on connector type.
| Connector | Impedance | Voltage Class | Safety Feature | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNC | 50 Ω / 75 Ω | Low-power | Standard | General lab/test; common for low-power lines. |
| MHV | — | Medium-power / High-voltage | Pins exposed | For HV where recessed contacts aren’t required. |
| SHV | — | High-voltage | Recessed contacts | Preferred for safety in disconnected condition. |